Blockchain Infrastructure Races to Match Sub-Second Block Times
Blockchain Infrastructure Races to Match Sub-Second Block Times
⚡ When milliseconds matter

Block times are accelerating across major networks. Solana, Base, and other L2s now push sub-second blocks, creating new demands for data infrastructure.
The challenge: Traditional indexing solutions struggle to keep pace with:
- Faster block production
- Traders relying on partial blocks
- Real-time data requirements
Substreams' approach:
- Processes blocks immediately as validating nodes make them available
- Streams transformed data in real-time
- Uses parallel execution to handle massive data chunks simultaneously
- Connects directly to Firehose for complete data capture
The shift to sub-second blocks represents a fundamental change in blockchain infrastructure requirements, moving beyond traditional one-block-at-a-time processing methods.
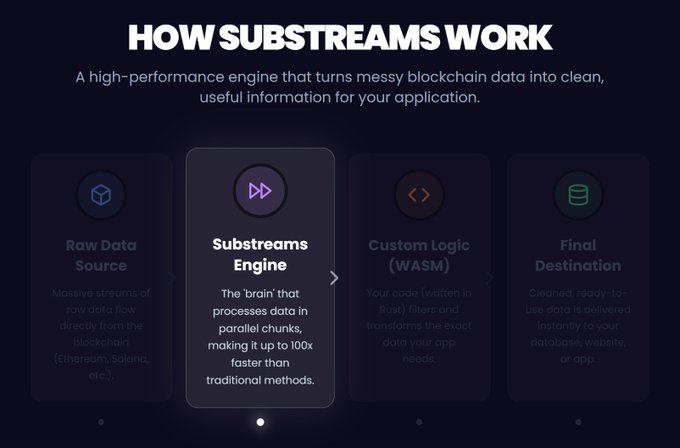
Wondering how Substreams work? Blockchains never sleep! Every second, thousands of transactions happen across networks like Ethereum, Solana, Arbitrum, BSC, and more. Substreams taps directly into Firehose, making sure no piece of information is missed. It’s the starting line
Think of the Substreams Engine as the ultimate speed booster. Instead of checking one block at a time, Substreams processes massive chunks of data all at once with parallel execution. This makes it faster than traditional methods, letting you sync years of history in minutes
The Invisible Infrastructure Powering Every Web3 Query
**Infrastructure operates best when invisible.** Every wallet balance check, DeFi transaction display, and app query relies on data infrastructure working silently behind the scenes. - The Graph has processed **trillions of queries** without fanfare - When infrastructure functions properly, users never notice it - When it fails, everything stops working This is the paradox of foundational technology: **success means obscurity.** The most critical systems are the ones we take for granted—until they're gone.
The Graph Deploys ERC-8004 Across 8 Chains for AI Agent Identity and Reputation
**The Graph has launched ERC-8004 Subgraphs across 8 blockchains**, creating a unified cross-chain directory for AI agent verification. **What ERC-8004 registers for AI agents:** - Identity (who they are) - Reputation (track record of behavior) - Validation (proof of correct task execution) **How it works:** An agent on Base can instantly verify the reputation of an agent on Arbitrum by querying a Subgraph. Without this infrastructure, every agent would need to scan raw blockchain data to check credentials, which would significantly slow down the network. This deployment provides the data layer that enables AI agents to function onchain at scale, working alongside payment rails like Coinbase's x402 for instant micropayments.
The Graph Emerges as Critical Infrastructure for Blockchain's Next Phase
As blockchain technology evolves, three major trends are converging around a single infrastructure need: - **Faster block times** across major chains require more efficient data indexing - **Institutional adoption** demands auditable, reliable blockchain data - **AI agents** need structured information to execute autonomous actions The Graph is positioning itself as the common solution to these challenges, providing the data infrastructure layer that enables: - Real-time access to blockchain information - Structured data formats for AI consumption - Auditable records for institutional compliance This convergence suggests data infrastructure may become as critical as the blockchains themselves, with The Graph serving as the connective tissue between chains, institutions, and autonomous agents.
Understanding x402 and ERC8004: New Token Standards Explained
The Graph has published an educational piece exploring **x402 and ERC8004**, emerging token standards in the Ethereum ecosystem. These experimental standards represent ongoing efforts to expand token functionality beyond traditional ERC-20 and ERC-721 formats. The article breaks down: - Technical specifications of x402 and ERC8004 - How these standards differ from existing token types - Potential use cases for developers - Implementation considerations The piece follows previous community interest in experimental token standards like ERC-404, which attempted to combine fungible and non-fungible token properties. [Read the full explanation](https://thegraph.com/blog/understanding-x402-erc8004/)
Substreams Sink SQL Adds Delta Updates for Faster Onchain Data Processing
Substreams Sink SQL now supports delta updates, improving how onchain data pipelines handle aggregations. **Key improvements:** - Aggregation logic moves to Postgres, reducing Substreams processing load - Enables native, incremental SQL operations (counts, sums, volumes) - Keeps data pipelines lighter and faster This update allows developers to perform database-level aggregations directly in Postgres rather than in Substreams modules. The change streamlines data processing by leveraging SQL's native capabilities for incremental calculations, making it easier to track metrics like transaction counts and trading volumes without additional overhead.